Arbeitsgruppe Dr. rer. nat. Florian Kurschus
Arbeitsgruppenleiter

Applications of master students interested in a research project are highly welcome.
Research Focus
We are interested in the development and regulation of inflammatory processes in autoimmunity and infection. Our animal models are skin inflammation models such as Imiquimod-induced dermatitis as model for psoriasis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as model for multiple sclerosis (MS). We are interested in the mechanism how pathogenic αβ and γδ T cells develop and are regulated. We use for our experiments genetically modified mice with conditional gene deletion or overexpression. Furthermore, we work with human samples and patient material. Our methods are largely immunological in vivo and in vitro methods. Flow cytometry plays a major role for our experiments for cell analysis and sorting.
Projects
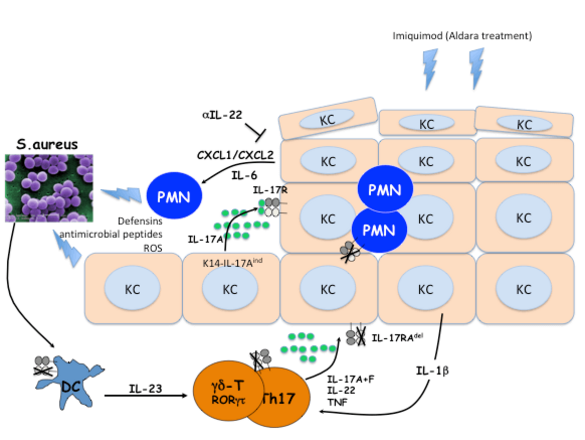
IL-17 signaling in the skin
In this project we analyze how dermal gd T cells in the skin are activated and expand in response to inflammatory stimuli. We are also investigating the role of the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) in psoriasis and in the Imiquimod-induced dermatitis as model. Funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
EBI2
One of our major projects is to define the impact of the G-protein coupled receptor EBI2 in inflammation and its implications for the human immune system especially in psoriasis and MS.
Funding
DFG: DISRUPT-MS - Uncovering the Mechanisms Driving Virus-Induced Central Nervous System Disease.
DFG: Entwicklung der Dysbiose in Mäusen mit Defizienz des IL-17
Signalweg in Keratinocytes
Group Members
Medizinische Doktoranden/-innen
Postdoc
Alumni
- Stefanos Voglis (MD thesis)
- Stephanie Gräf (PhD thesis)
- Dr. rer. nat. Florian Wanke (PhD)
- André Heinen (Technician and Bachelor thesis)
- Dr. med. Morad Zayoud (MD thesis)
- Dr. med. Khalifa El-Malki (MD thesis)
- Dr. rer. nat. Daniele Ielo (PhD)
- Sarah Kehr (Bachelor thesis)
- Sonja Moos
- Lucas Arendholz
- Julius Schwingen
- Mustafa Kaplan
Selected Publications
- Moos S, Regen T, Wanke F, Tian Y, Arendholz LT, Hauptmann J, Heinen AP, Bleul L, Bier K, El Malki K, Reinhardt C, Prinz I, Diefenbach A, Wolz C, Schittek B, Waisman A, Kurschus FC. IL-17 Signaling in Keratinocytes Orchestrates the Defense against Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infection. J Invest Dermatol. 2023 Jul;143(7):1257-1267.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.01.016.
- Moos S, Mohebiany AN, Waisman A, Kurschus FC*.Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis in Mice Depends on the IL-17 Signaling of Keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2019 May;139(5):1110-1117.
- Wanke F, Moos S, Croxford AL, Heinen AP, Gräf S, Kalt B, Tischner D, Zhang J, Christen I, Bruttger J, Yogev N, Tang Y, Zayoud M, Israel N, Karram K, Reißig S, Lacher SM, Reichhold C, Mufazalov IA, Ben-Nun A, Kuhlmann T, Wettschureck N, Sailer AW, Rajewsky K, Casola S*, Waisman A*, and Kurschus FC*. EBI2 is highly expressed in multiple sclerosis lesions and promotes early CNS migration of encephalitogenic CD4 T cells. Cell Reports. 2017 Jan 31;18(5):1270-1284.
- Croxford AL, Karbach S, Kurschus FC, Wörtge S, Nikolaev A, Yogev N, Klebow S, Schuler R, Reissig S, Piotrowski C, Brylla E, Bechmann I, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Wunderlich FT, Munzel T, von Stebut E, Waisman A. IL-6 Regulates Neutrophil Microabscess Formation in IL-17A-Driven Psoriasiform Lesions. J Invest Dermatol 2014;134:728-35.
- El Malki K, Karbach SH*, Huppert J, Zayoud M, Reissig S, Schüler R, Nikolaev A, Karram K, Münzel T, Kuhlmann CR, Luhmann HJ, von Stebut E, Wörtge S, Kurschus FC*, Waisman A. An alternative pathway of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in the absence of interleukin-17 receptor a signaling. J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Feb;133(2):441-51.
- Yogev N, Frommer F, Lukas D, Kautz-Neu K, Karram K, Ielo D, von Stebut E, Probst HC, van den Broek M, Riethmacher D, Birnberg T, Blank T, Reizis B, Korn T, Wiendl H, Jung S, Prinz M, Kurschus FC, Waisman A. Dendritic cells ameliorate autoimmunity in the CNS by controlling the homeostasis of PD-1 receptor(+) regulatory T cells. Immunity. 2012 Aug 24;37(2):264-75.
- Kurschus FC*, Croxford AL, Heinen AP, Wörtge S, Ielo D, Waisman A. Genetic proof for the transient nature of the Th17 phenotype. Eur J Immunol. 2010 Dec;40(12):3336-46.
- Pöllinger B, Krishnamoorthy G, Berer K, Lassmann H, Bösl MR, Dunn R, Domingues HS, Holz A, Kurschus FC*, Wekerle H*. Spontaneous relapsing-remitting EAE in the SJL/J mouse: MOG-reactive transgenic T cells recruit endogenous MOG-specific B cells. J Exp Med. 2009 Jun 8;206(6):1303-16.
- Kurschus FC, Fellows E, Stegmann E, Jenne DE. Granzyme B delivery via perforin is restricted by size, but not by heparan sulfate-dependent endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 16;105(37):13799-804.
- Fellows E, Gil-Parrado S, Jenne DE, Kurschus FC*. Natural killer cell-derived human granzyme H induces an alternative, caspase-independent cell-death program. Blood. 2007 Jul 15;110(2):544-52.
- Kurschus FC*, Bruno R, Fellows E, Falk CS, Jenne DE. Membrane receptors are not required to deliver granzyme B during killer cell attack. Blood. 2005 Mar 1;105(5):2049-58.
*corresponding authorship